Throughout history, human civilizations have risen and fallen, leaving behind tantalizing traces of their existence and achievements. Among the most captivating aspects of these ancient societies is the wealth of knowledge they possessed—much of which has been lost to the sands of time. This article delves into the mysteries of ancient civilizations and the lost knowledge that continues to intrigue and inspire modern researchers.

The Enigmatic Ancient Egyptians
One of the most well-known ancient civilizations is that of Egypt. Flourishing along the Nile River for millennia, the ancient Egyptians made remarkable advancements in various fields. Their knowledge of mathematics, engineering, and astronomy enabled them to construct monumental structures like the pyramids and the Sphinx, feats that continue to baffle scientists and historians.
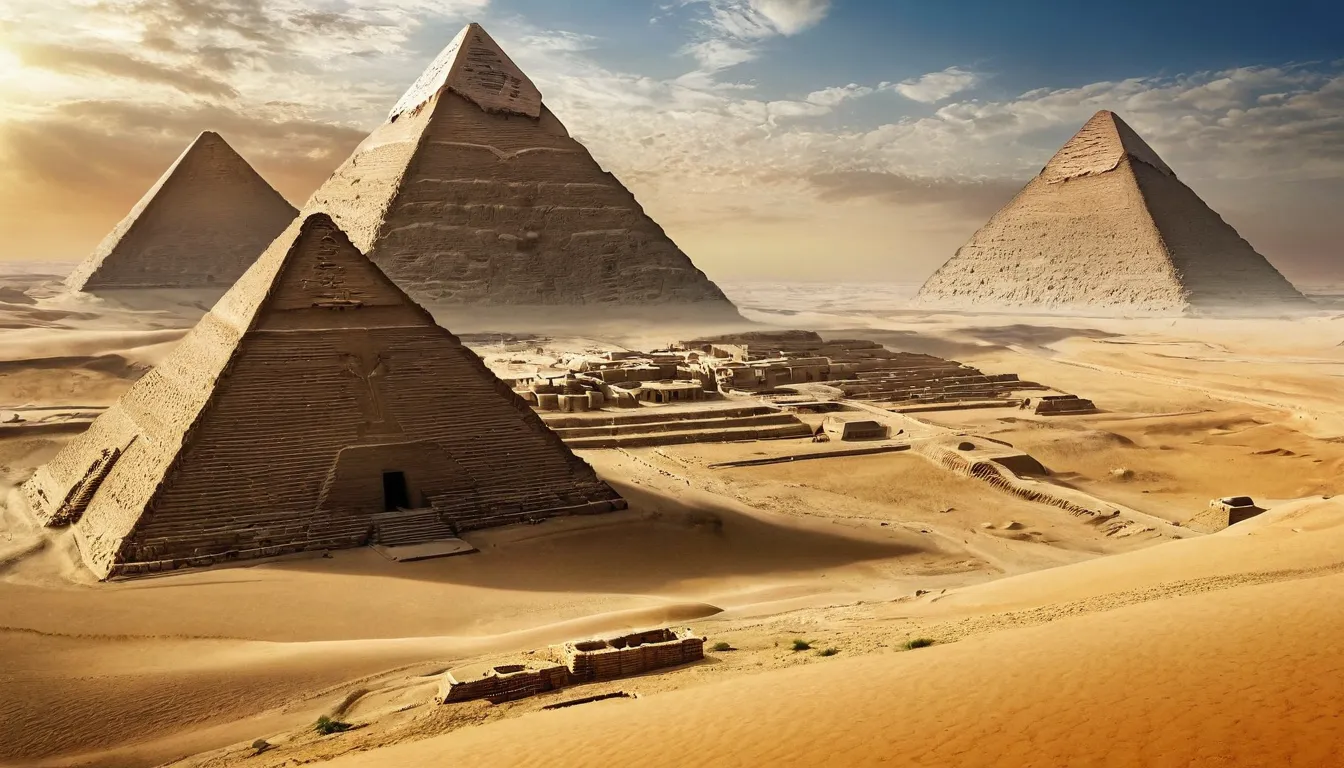

The ancient Egyptians also developed a sophisticated system of medicine. The Ebers Papyrus, dating back to around 1550 BCE, reveals a deep understanding of anatomy and medical practices. However, much of this knowledge was lost following the decline of their civilization. Modern medicine could benefit immensely from fully uncovering and understanding these ancient practices.
The Intellectual Legacy of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is often regarded as the cradle of Western civilization, having laid the intellectual foundations for much of modern science, philosophy, and politics. Thinkers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle explored profound questions about existence, ethics, and the nature of knowledge itself. Their works continue to influence contemporary thought, but there remains a significant portion of Greek philosophical and scientific works that have been lost over time.
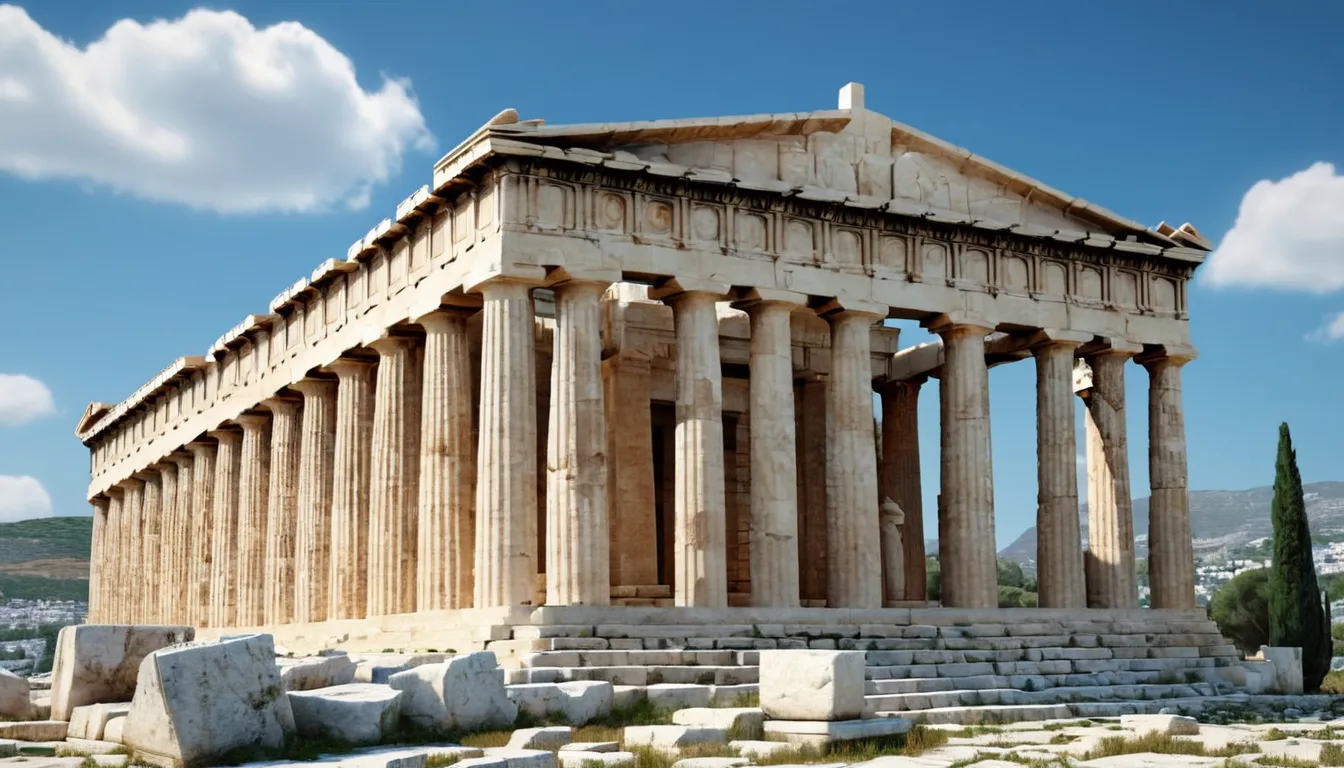

The Library of Alexandria, one of the most famous repositories of ancient knowledge, housed countless scrolls and texts from all over the ancient world. The destruction of this library, often attributed to several historical events including fires and wars, represents a colossal loss of ancient knowledge. Reconstructing even a fraction of its contents could revolutionize our understanding of ancient Greek and Egyptian contributions to various fields.
The Advanced Astronomy of the Maya
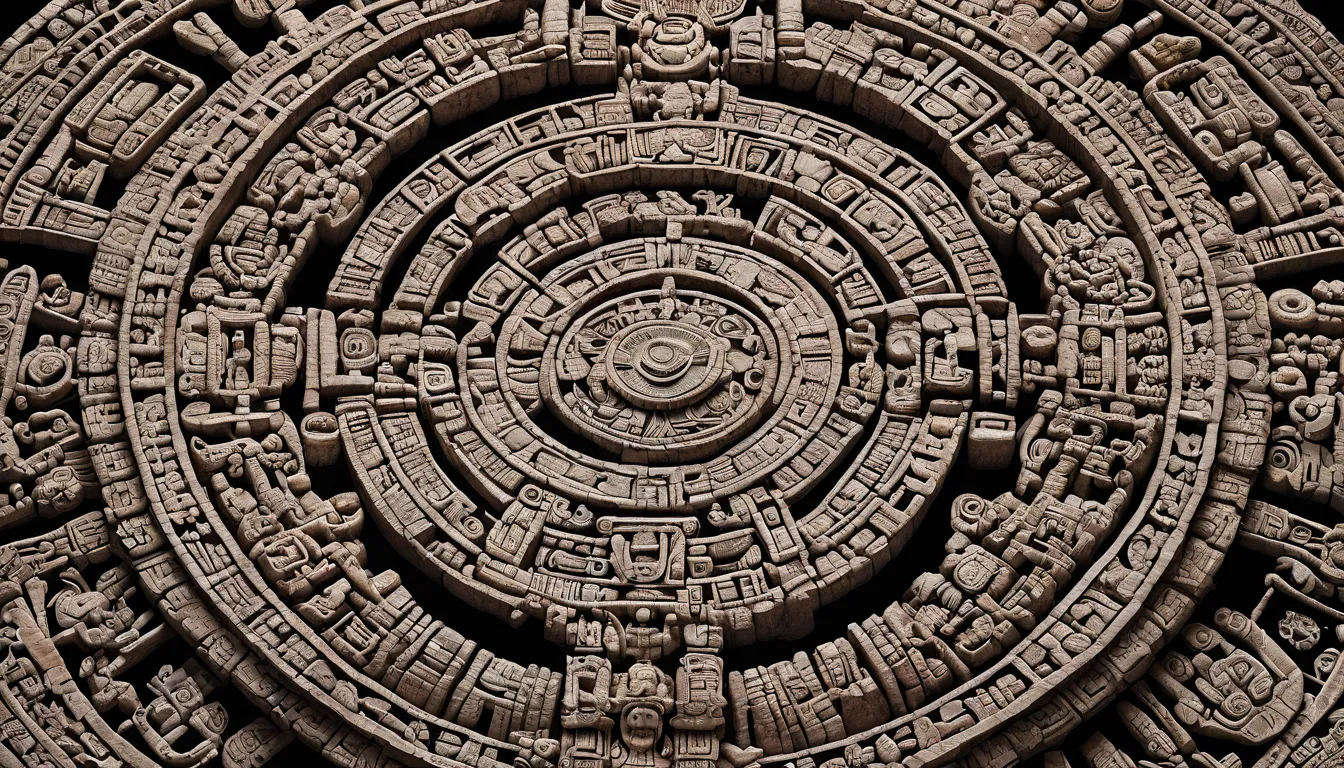
The Maya civilization, which flourished in Mesoamerica from around 2000 BCE to the 16th century CE, possessed an extraordinary understanding of astronomy and mathematics. They developed a complex calendar system and could predict celestial events with remarkable accuracy. The Dresden Codex, one of the few surviving Maya books, reveals their sophisticated astronomical knowledge, including detailed records of solar and lunar cycles.
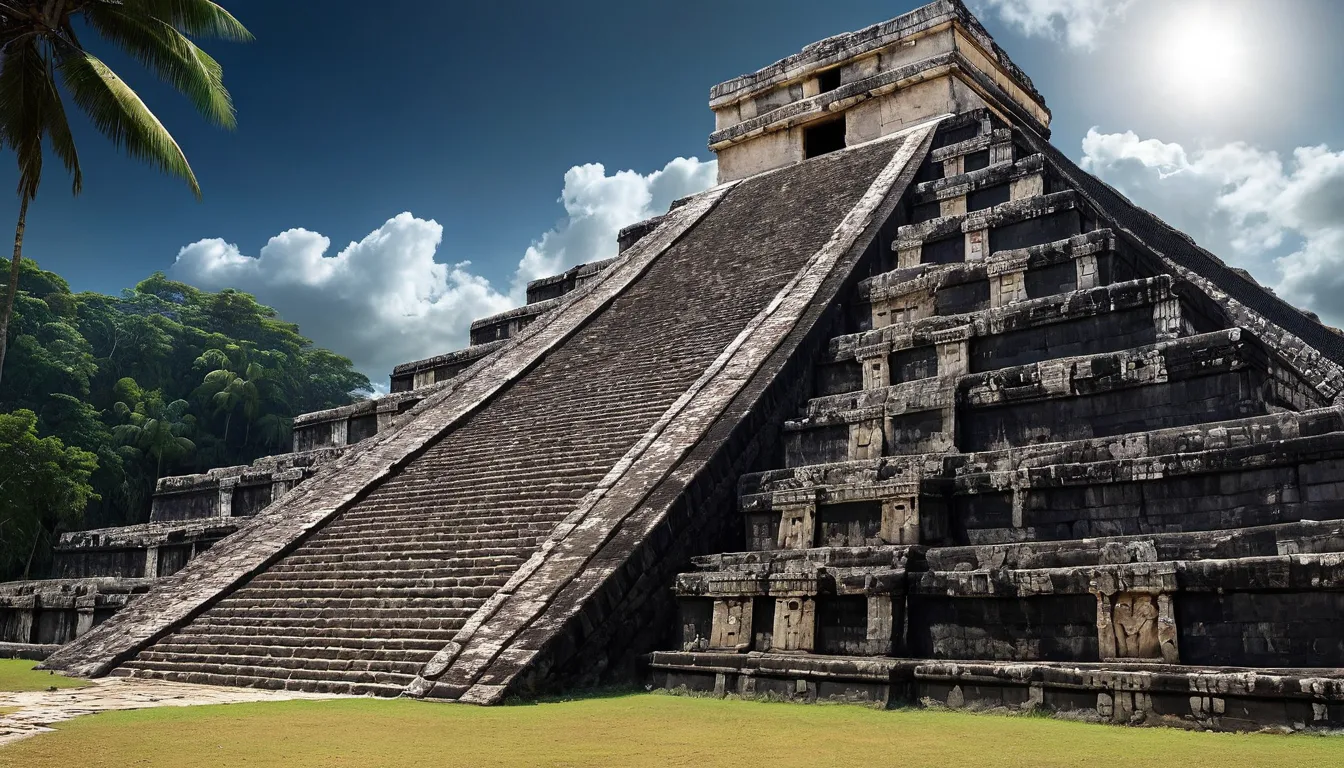

Despite these advancements, much of Maya knowledge was lost during the Spanish conquest. The burning of Maya codices by Spanish priests, who deemed them heretical, resulted in the loss of countless records and insights. Efforts to decipher the remaining texts and uncover the depths of Maya knowledge continue to this day, offering glimpses into their advanced understanding of the cosmos.

The Engineering Marvels of Ancient Rome
The Roman Empire, known for its engineering prowess, left behind a legacy of architectural and infrastructural marvels. The construction of aqueducts, roads, and monumental structures like the Colosseum and the Pantheon demonstrate their advanced understanding of engineering and construction techniques.
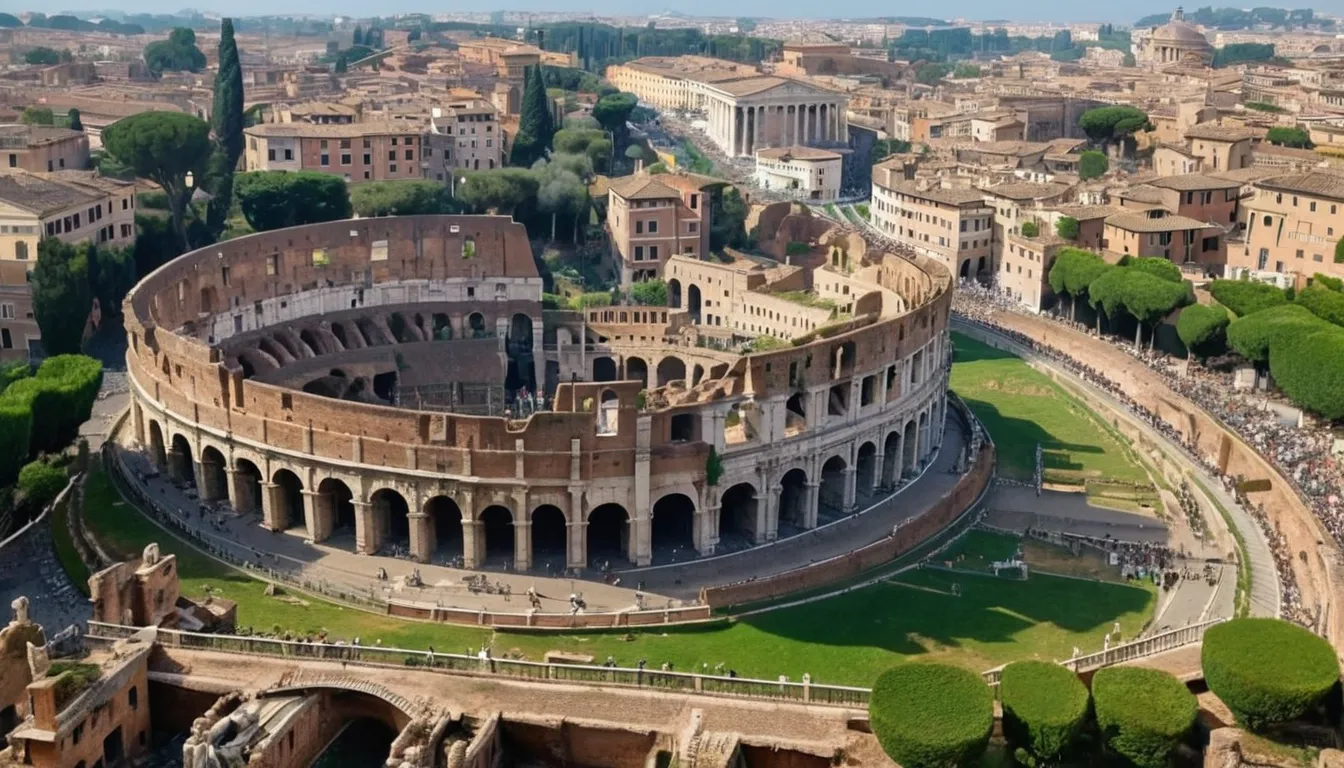

Roman engineering was not limited to grand structures. The Romans also developed sophisticated systems for urban planning, water management, and public health. The loss of Roman engineering knowledge following the fall of the Western Roman Empire led to a period of technological stagnation in Europe, often referred to as the Dark Ages. The rediscovery and study of Roman engineering principles during the Renaissance helped propel Europe into the modern era.
The Indus Valley Civilization’s Urban Planning
The Indus Valley Civilization, which thrived around 2500 BCE in what is now Pakistan and northwest India, is notable for its advanced urban planning and sophisticated civil engineering. Cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa were characterized by well-planned streets, advanced drainage systems, and impressive public baths, indicating a high level of social organization and technological skill.
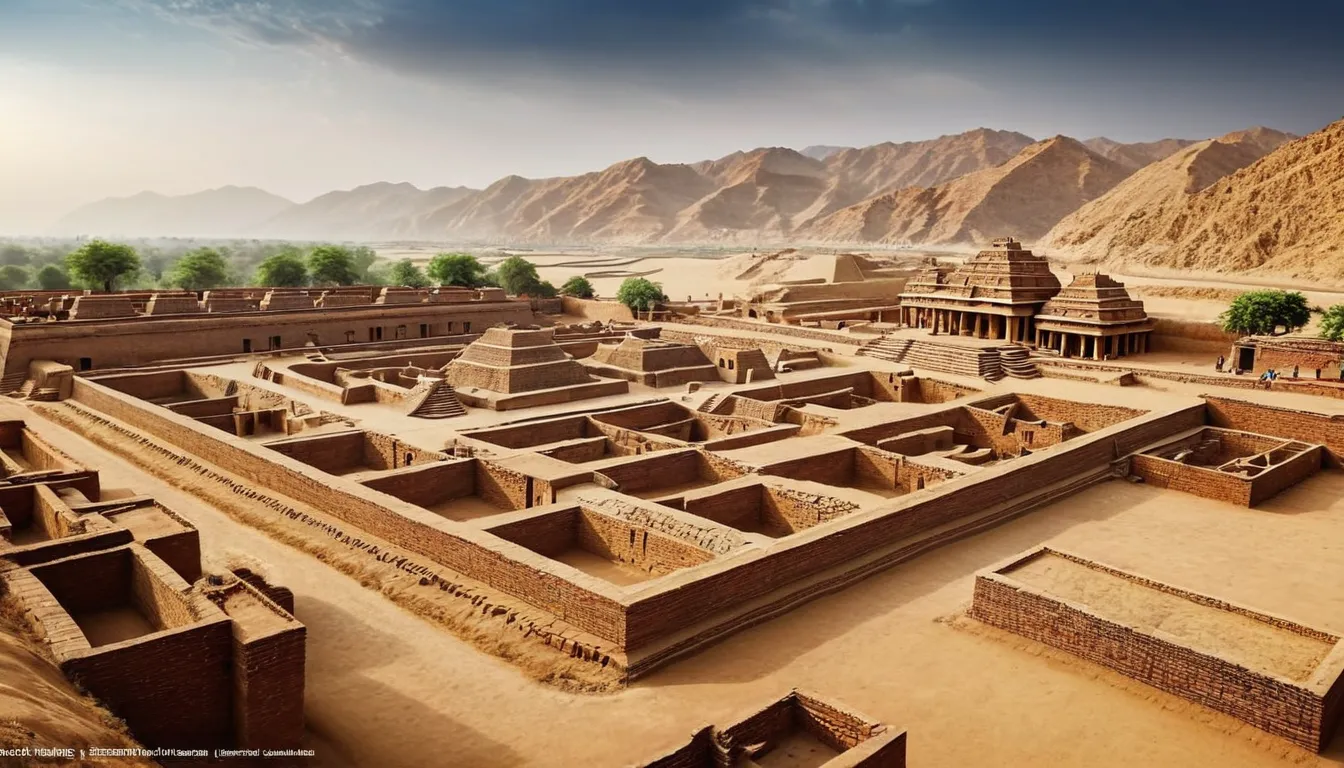

Despite these achievements, the script of the Indus Valley Civilization remains undeciphered, and much of their knowledge and cultural practices are still shrouded in mystery. The loss of their written records means that significant aspects of their technological and societal advancements remain unknown, leaving modern scholars to piece together their history from archaeological findings alone.
The Lost Arts of the Ancient Chinese
Ancient China, with its long history and numerous dynasties, contributed significantly to global knowledge and innovation. The Chinese were pioneers in fields such as astronomy, medicine, metallurgy, and engineering. Inventions like papermaking, gunpowder, and the compass originated in ancient China and had profound impacts on the world.

However, many ancient Chinese texts and artifacts have been lost due to wars, political turmoil, and natural disasters. The burning of books and burial of scholars under the Qin Dynasty and the destruction during the Cultural Revolution in the 20th century are notable examples of such losses. Rediscovering and preserving ancient Chinese knowledge remains a crucial task for historians and archaeologists.
Conclusion: The Quest for Lost Knowledge
The study of ancient civilizations and their lost knowledge is more than an academic exercise; it is a journey to understand humanity’s shared heritage. Each discovery, whether it be a fragment of a text, a buried artifact, or a newly deciphered inscription, brings us closer to comprehending the full scope of ancient human achievement.

Modern technology, including satellite imagery, advanced archaeological methods, and digital reconstruction, offers new ways to uncover and preserve ancient knowledge. As we continue to explore and interpret the remnants of these ancient civilizations, we gain not only historical insights but also inspiration and wisdom that can inform and enrich our present and future.
The lost knowledge of ancient civilizations serves as a reminder of the fragility of human achievements and the enduring quest to learn from our past. By valuing and studying these ancient contributions, we honor the legacy of our ancestors and ensure that their wisdom is not entirely lost to time.